# The Middle Ear
The middle ear refers to a collection of bones (ossicles) and muscles which are contained within the tympanic cavity.
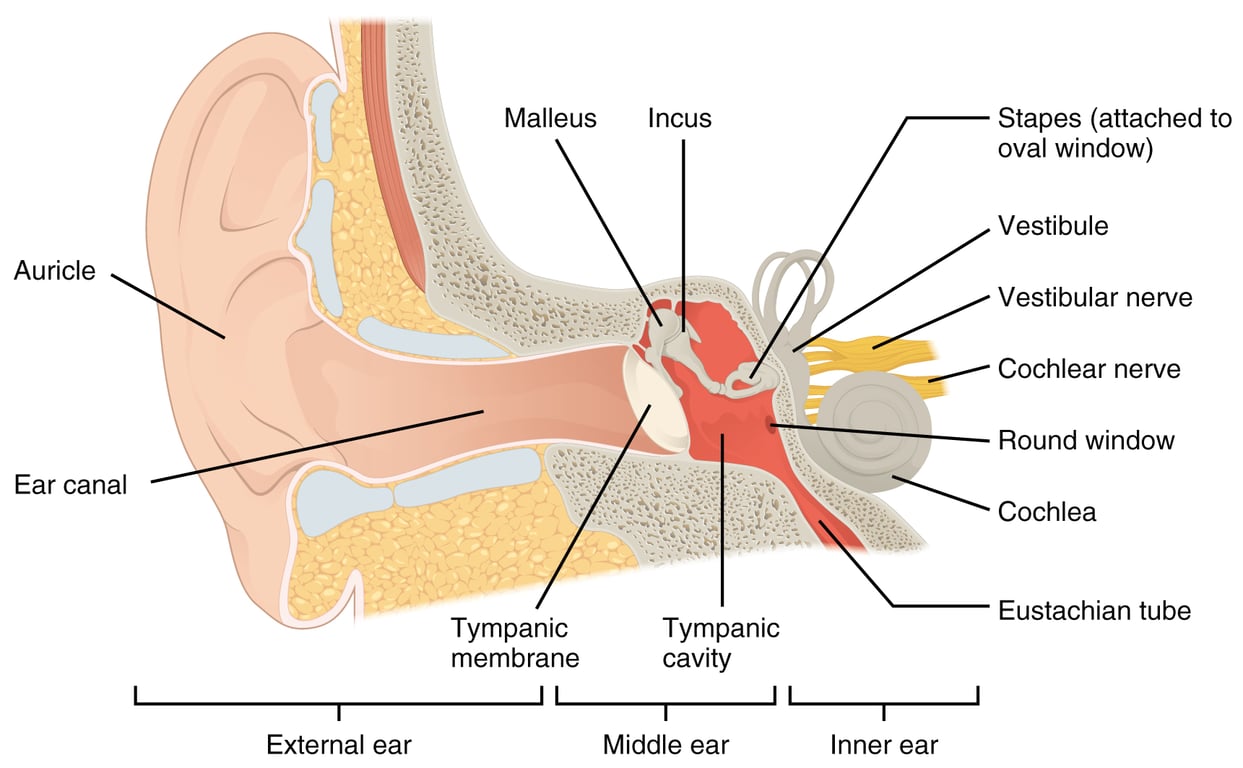
## The Eardrum (Tympanic Membrane)
Air pressure waves are transformed into physical vibrations, which are amplified in the middle ear and transferred to the cochlea (see the diagram above).
## The Ossicles
The ossicles attach the eardrum and form the ossicular chain, which is made up of 3 bones:
- Malleus
- Incus
- Stapes
These bones serve as a mechanical amplifier depending on the frequencies that are entering the ear canal.
## Eustachian Tube
The eustachian tube is a narrow passage that goes from the pharynx to the tympanic cavity. This passage is what allows the middle ear to remain "equalized" with the outside pressure.
## Pressure Changes
During normal flight, pressure decreases during a climb and increases during a descent. The pressure changes need to be "equalized" via the eustachian tubes when these changes in pressure occur. For most healthy individuals, this will only cause a mild discomfort. However, there are many situations where a person can experience pain from these changes.
## Ear Block
When the eustachian tubes become blocked, they are no longer able to transfer pressure into our out of the middle ear. This condition is referred to as ear block.
Common causes of ear block include bacterial and viral infections. This is another reason why flying while even mildly sick can be hazardous.
### Symptoms Related to Ear Block
The following symptoms are common when experiencing ear block:
- Pain
- Vertigo
- Disorientation
- Headache
- Hearing
All of these symptoms can be distracting and cause a pilot to lose focus on flying the airplane safely. Additionally, if a passenger is suffering from ear block, make sure to assist, but do not lose focus on flying.
### Treatment of Ear Block
The following treatments can be effective in returning the inner ear to ambient pressure:
- Swallowing
- Yawning
- Tensing muscles in the throat
- Pinch nose and attempt to blow out through nostrils (valsalva maneuver)
Remember that suffering from ear block during a climb will most likely result in similar problems when descending.
---
# The Sinuses

Sinuses are simply cavities in your head which are connected by narrow passageways. The sinuses make mucus that drain out of your nose. Similar to ear block, these passages can become blocked by inflammation or an excessive amount of mucus production.
## Sinus Block
When the sinuses are unable to equalize to the outside air pressure, they become blocked. This can be incredibly painful. Symptoms include:
- Facial pain or pressure
- Nasal congestion
- Nasal discharge (possibly bloody)
- Sinus headache
- Reduced sense of smell and taste
- Coughing
## Preventative Measures to Reduce Risk of Sinus Block
It is important to always stay hydrated, especially before and during a flight. This will help to thin the mucus in the sinus cavities and promote discharge.
Additionally, avoid anything that could cause an allergic reaction, as this will cause the sinuses to become inflamed.
## Dealing with Sinus Block in Flight
- Make sure to drink plenty of water immediately if you begin to feel symptoms of sinus block
- Chew and swallow something as this will help to equalize the pressure
- Stay upright. This will promote sinus drainage and allow the sinus cavities to equalize